One quarter of the military population experienced food insecurity in 2018 and 2020
- by Matthew P. Rabbitt
- 5/2/2024
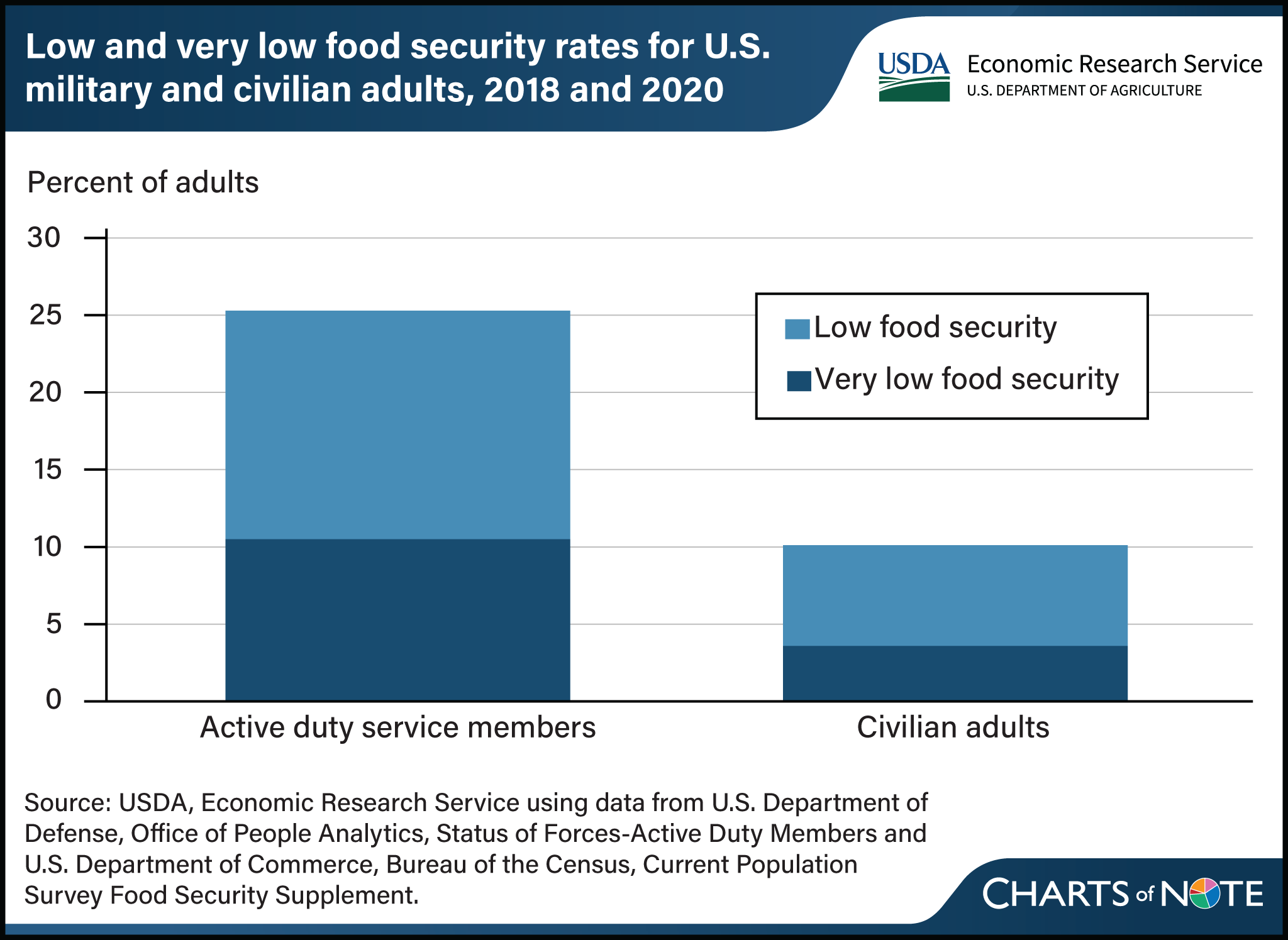
In 2018 and 2020, 25.3 percent of the military population reported experiencing food insecurity, or low and very low food security, compared with 10.1 percent in the demographically equivalent civilian adult population. Food security—defined as access to enough food for an active, healthy life at all times—is associated with cognitive function, body mass index, and intentions to stay in the military. Further, 10.5 percent of the military population reported the more severe form of food insecurity, very low food security, in 2018 and 2020. During the same period, the civilian adult population reported very low food security of 3.6 percent. USDA, Economic Research Service (ERS) monitors the food security status of households in the United States through an annual nationwide survey, which provided the civilian adult data. Military data were drawn from the Status of Forces Survey of Active Duty Members. These findings indicate that the military population experiences elevated rates of food insecurity compared with the general population. This chart appears in the ERS report Comparing Food Insecurity Among the U.S. Military and Civilian Adult Populations, published in April 2024.

