Imports of fresh and processed vegetables make up an increasing share of domestic consumption
- by Alex Melton and Travis Minor
- 4/13/2017
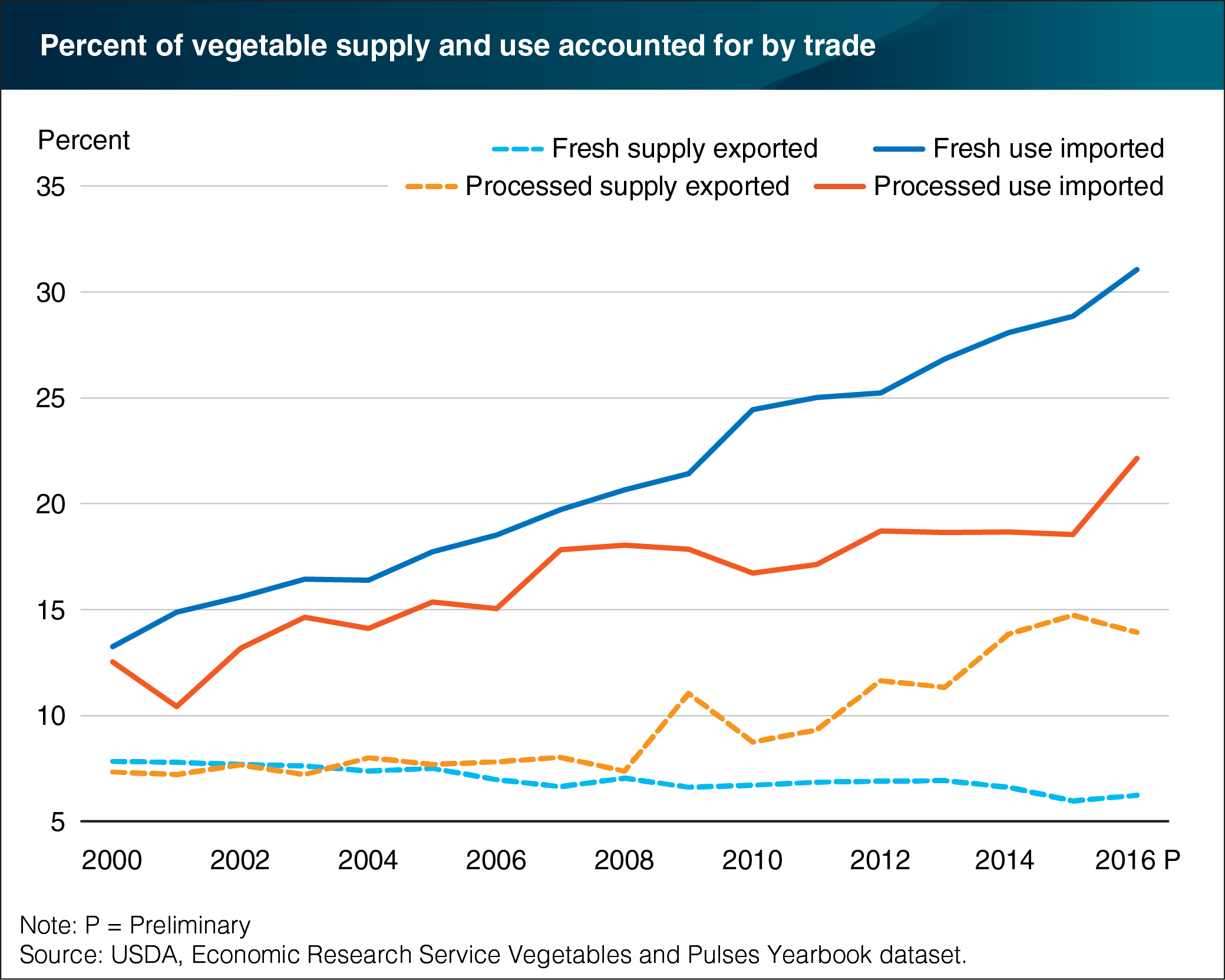
Trade plays a vital part in both fresh and processed vegetable markets, one that has increased over time. The United States imports a larger amount of fresh and processed vegetables than it exports. This is in contrast with U.S. agricultural trade as a whole, which consistently runs a trade surplus (exports exceed imports). In 2000, fresh and processed vegetable imports represented 12 percent of domestic use each. By 2016, the import share of domestic use had increased to over 30 percent for fresh vegetables and 22 percent for processed vegetables. The export market for vegetables has grown at a slower pace. Processed vegetable exports doubled between 2000 and 2016 from 7 to 14 percent of domestic use, while fresh vegetables decreased from 7 percent in 2000 to 6 in 2016. Growth in vegetable and other food commodity imports has been driven by expanding domestic demand and reduced trade costs like shipping and tariffs. Consumer preferences for year-round availability of seasonal foods and for vegetables not commonly grown domestically have also played a role in rising import shares. Cucumbers, tomatoes, and peppers are predominantly supplied by imports, while cauliflower has the largest export share. This chart is drawn from data in the annual ERS Vegetables and Pulses Yearbook tables updated in April 2017.

