The production of five popular vegetables relies on foreign labor
- by Skyler Simnitt
- 6/29/2020
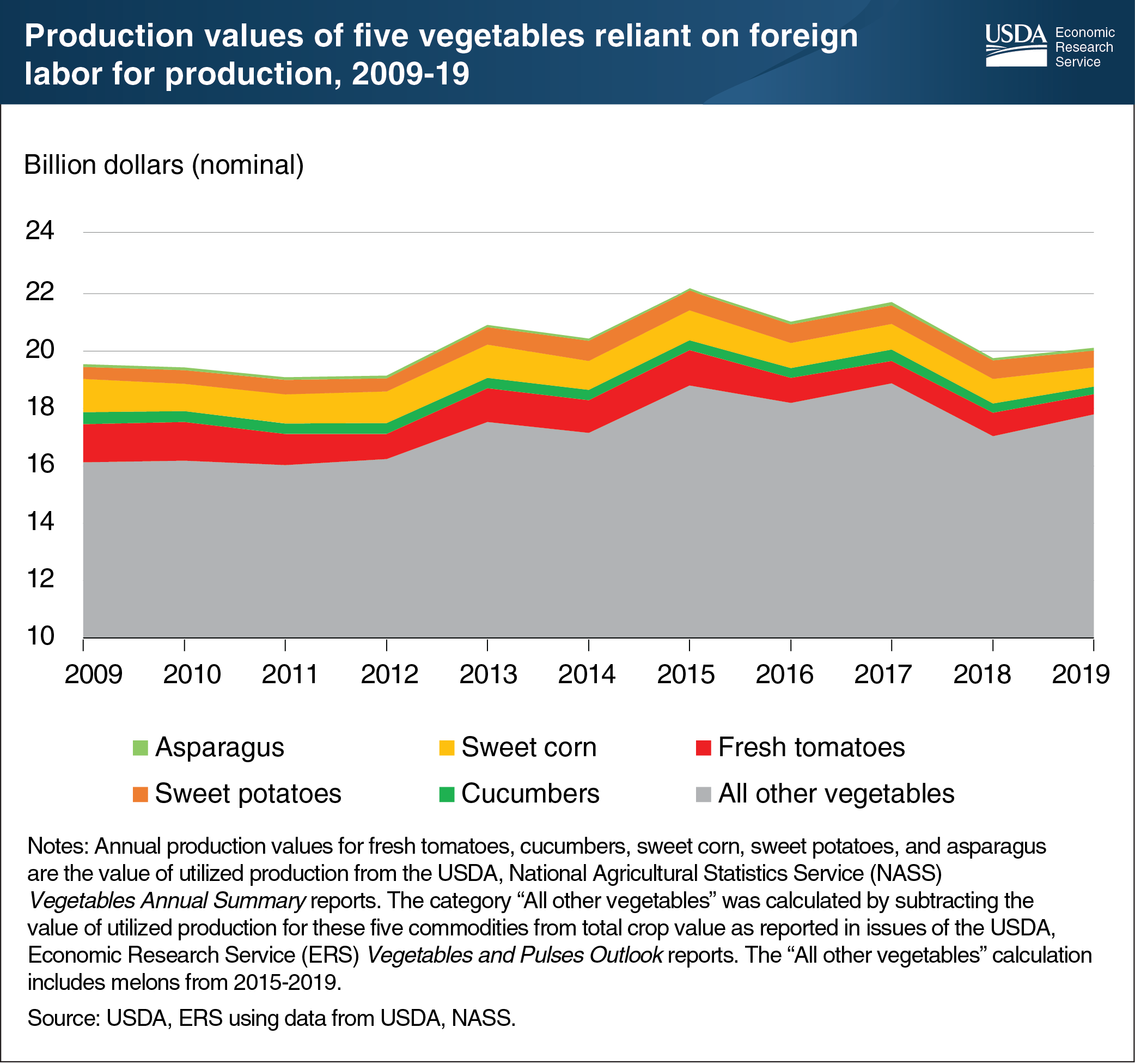
In 2019, tomatoes for the fresh market, harvested by hand, were valued at $705 million, while sweet corn production, typically harvested by hand or machine, was valued at $652 million, and sweet potatoes, for which workers are required for machine operation and post-harvest handling, was valued at $588 million. The production of these and other vegetables grown in the United States may be affected by disruptions of foreign labor flows. An estimated 10 percent of all hired farm workers are foreign nationals employed on temporary work visas under the H-2A agricultural workers program. Restrictions that affected the issuance of new H-2A visas at U.S. consulates starting March 18, 2020, were relaxed on April 20, 2020, which may have alleviated shortages of available workers. H-2A application disclosure data through the second quarter of fiscal year 2020 revealed that a significant majority of the H-2A workers with job start dates of mid-March or later had been hired as laborers for asparagus, sweet potatoes, sweet corn, cucumbers, and tomatoes. These five vegetable commodities, therefore, are among those most likely to be affected by a short-term reduction in the inflow of H-2A workers. Together, these vegetables accounted for 12 percent of the total production value of U.S. vegetables in 2019. This chart is based on the Economic Research Service’s Vegetables and Pulses Outlook reports and H-2A application disclosure data from the Department of Labor.

