Fast food plays a larger role in all children's diets, but school food remains relatively more important for lower income children
- by Joanne Guthrie
- 8/23/2016
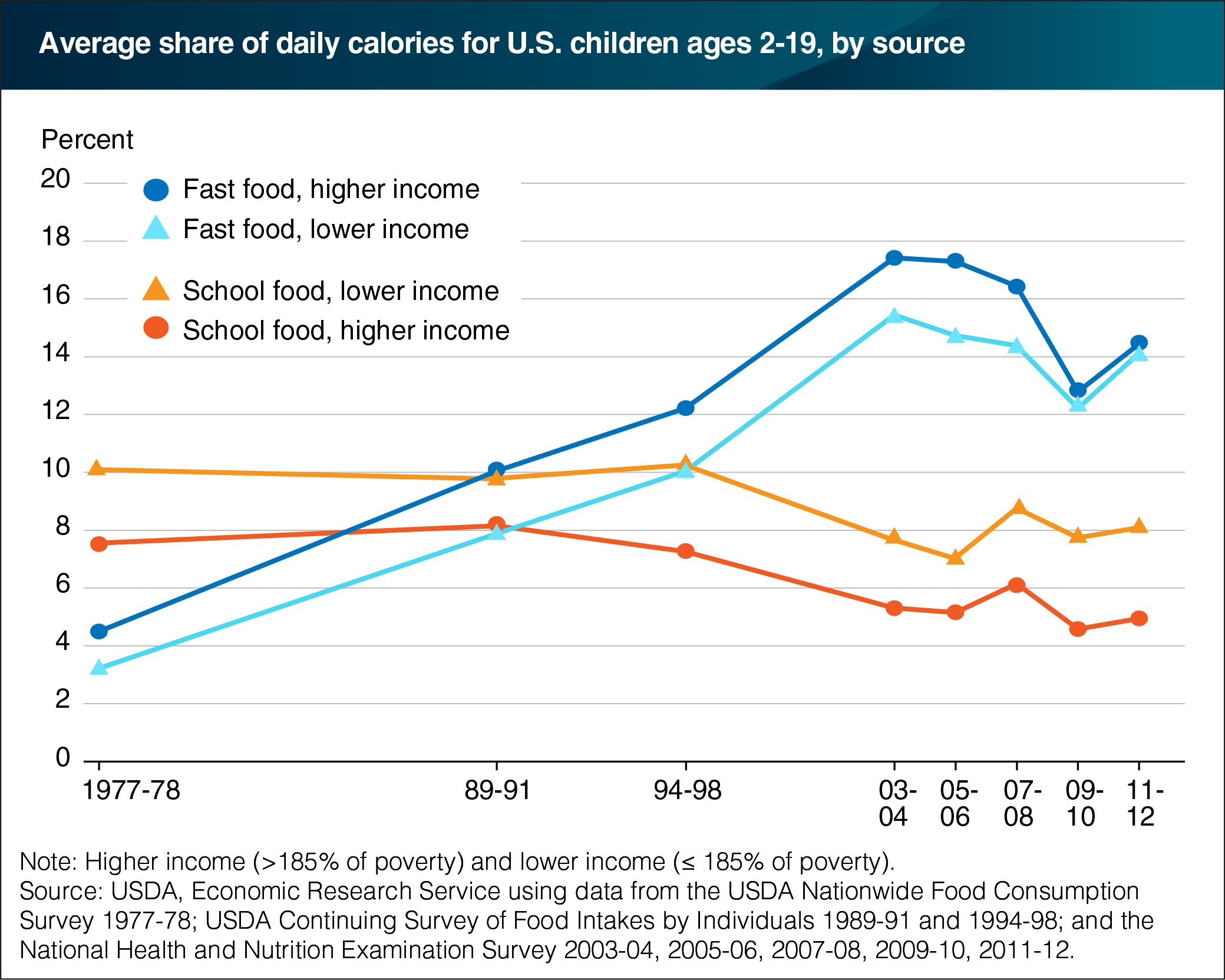
Federal food intake surveys conducted between 1977 and 2012 reveal that, in the 1990s, fast food overtook school food as the largest source of food prepared away from home in children’s diets. However, school foods have remained a more important source of calories for lower income children than for higher income children. The mandated cutoff for free or reduced-price USDA school meals is a household income at or below 185 percent of the Federal poverty level. In 1977-78, school meals provided 10.1 percent of the calories consumed by lower income children eligible for free or reduced-price school breakfasts and lunches and 7.5 percent of higher income children’s total calories. In that same year, fast food provided 4.5 percent of higher income children’s average daily energy intake and 3.2 percent of lower income children’s calories. School food continued to provide about 10 percent of lower income children’s total calories in 1994-98 but, by 2011-12, the school food share fell to 8.1 percent and the fast food share rose to 14.2 percent. This chart appears in “Linking Federal Food Intake Surveys Provides a More Accurate Look at Eating Out Trends” in the June 2016 issue of ERS’s Amber Waves magazine.
We’d welcome your feedback!
Would you be willing to answer a few quick questions about your experience?

