Most nonfarm income of farm households comes from wages & salaries
- by Economic Research Service
- 12/17/2014
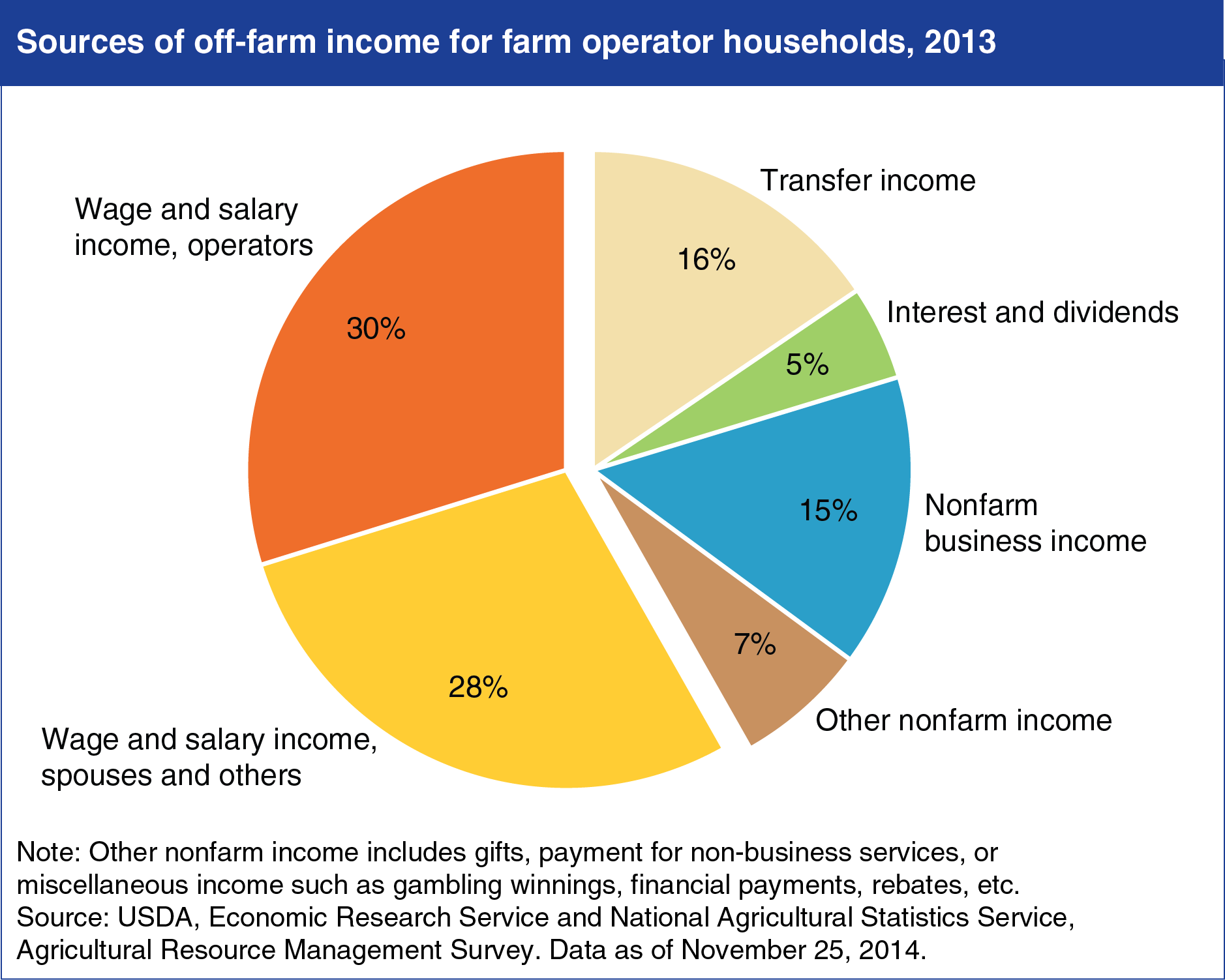
In 2013, only about one-quarter of total farm household income came from farming. Because of the broad USDA definition of a farm (which includes places with the potential for as little as $1,000 in annual sales), more than half of farm operator households consistently incur a net loss from farming activities in any given year, and far more do not earn the equivalent of a market wage for their on-farm labor. As a result, most farm operator households rely heavily on off-farm income. Of the total off-farm income earned by all farm operator households, the majority comes from wages and salaries earned by household members through nonfarm jobs, followed by income transfers (e.g., Social Security) and profits from nonfarm businesses owned by farm household members. As a group, U.S. farm operator households earn their income from a wide range of activities, reflecting the diverse set of skills, knowledge, and economic goals held by farm operators and their families. This chart is found in the ERS topic page, Farm Household Well-Being, updated November 2014.

