Agricultural Act of 2014 maintains SNAP's basic eligibility guidelines
- by Laura Tiehen
- 3/26/2014
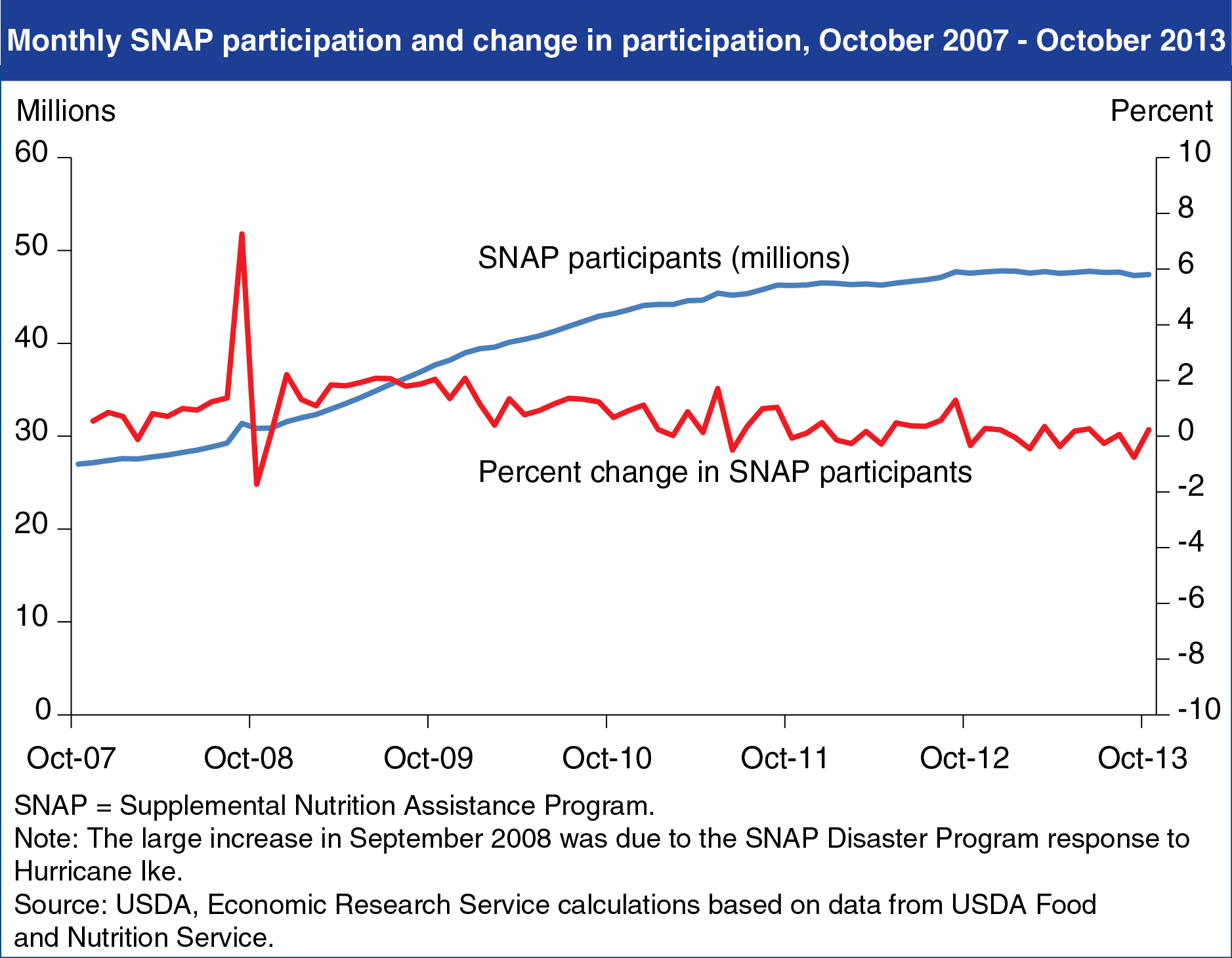
The new U.S. farm bill—the Agricultural Act of 2014—reauthorizes the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), the Nation’s largest food and nutrition assistance program. In fiscal 2013, Federal spending for the program totaled $79.8 billion and an average of 47.6 million people per month received SNAP benefits. The Act maintains the program’s basic eligibility guidelines, and States retain the option, within Federal guidelines, to coordinate SNAP eligibility requirements with the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program. Historical evidence suggests that SNAP expenditures will decline even without stricter eligibility limits, as caseloads contract in response to improving economic conditions. In fact, growth in monthly participation has slowed since late 2009. The Act restricts access to an income deduction related to home heating and cooling costs that boosted SNAP benefits for some households. The Act also provides additional SNAP funding for enhanced employment and training activities for SNAP recipients, expanded efforts to prevent SNAP trafficking (the illegal exchange of SNAP benefits for cash), and matching funds for projects that encourage SNAP recipients to purchase fruits and vegetables by reducing their cost. Find this chart and additional information on ERS’s Agricultural Act of 2014: Highlights and Implications web pages.
We’d welcome your feedback!
Would you be willing to answer a few quick questions about your experience?

