The U.S. agricultural sector, including its electricity consumption, accounted for an estimated 10.5 percent of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2022
- by Ron Sands
- 5/13/2024
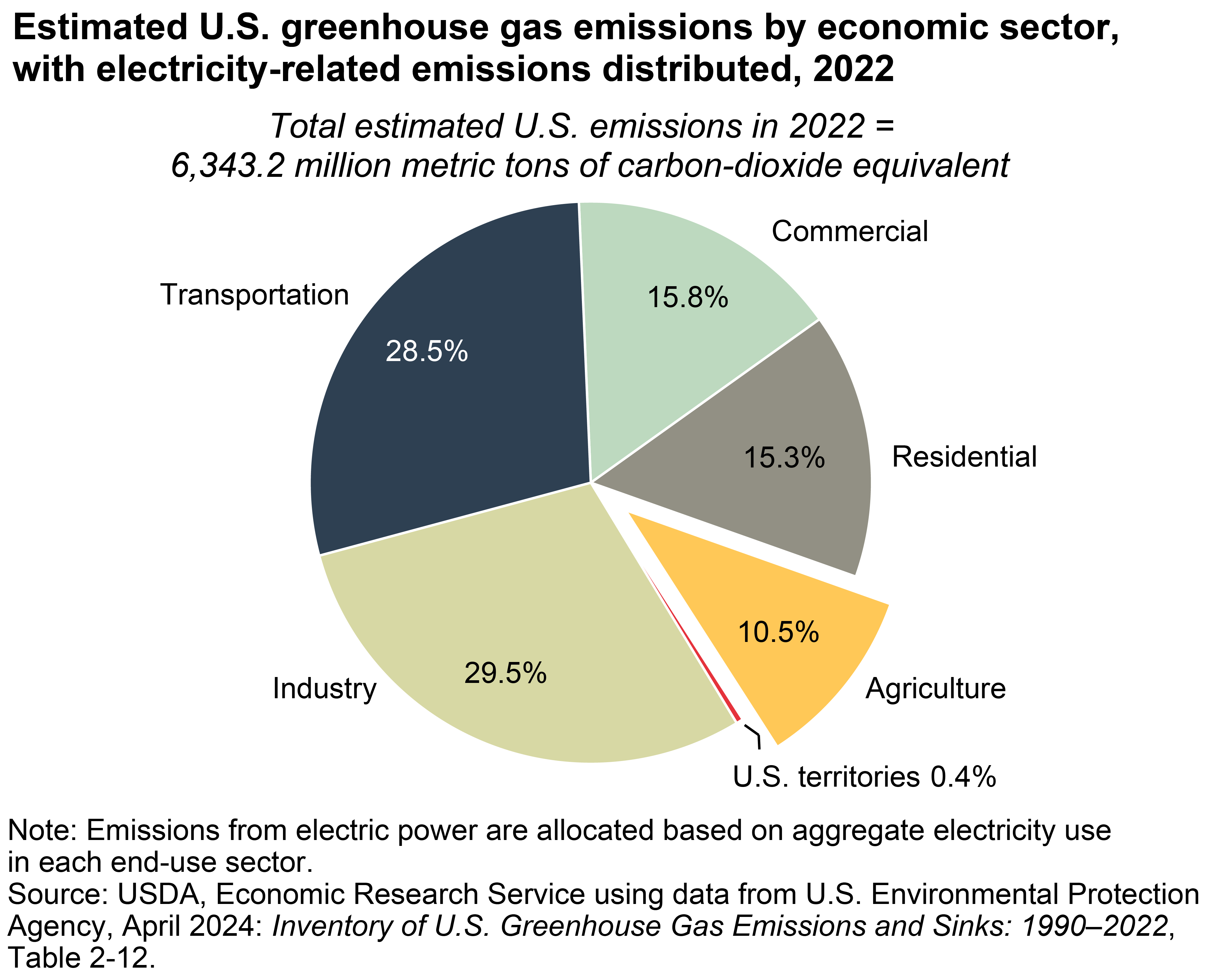
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimated that the agricultural sector, including its electricity consumption, accounted for 10.5 percent of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2022. Globally, carbon dioxide emissions are the largest contributor to climate change. However, the emissions profile for agriculture differs from that of the overall economy. In agriculture, crop and livestock activities emit nitrous oxide and methane, mainly from fertilizer application, enteric fermentation (a normal digestive process in animals that produces methane), and manure storage and management. Between 1990 and 2022, estimated greenhouse gas emissions from the U.S. agricultural sector have increased by approximately 5.1 percent. During the same period, estimated total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions have declined by 3.0 percent.
