Demand for domestic vegetable oils boosted by rising biofuels production
- by Maria Bukowski and Bryn Swearingen
- 1/30/2024
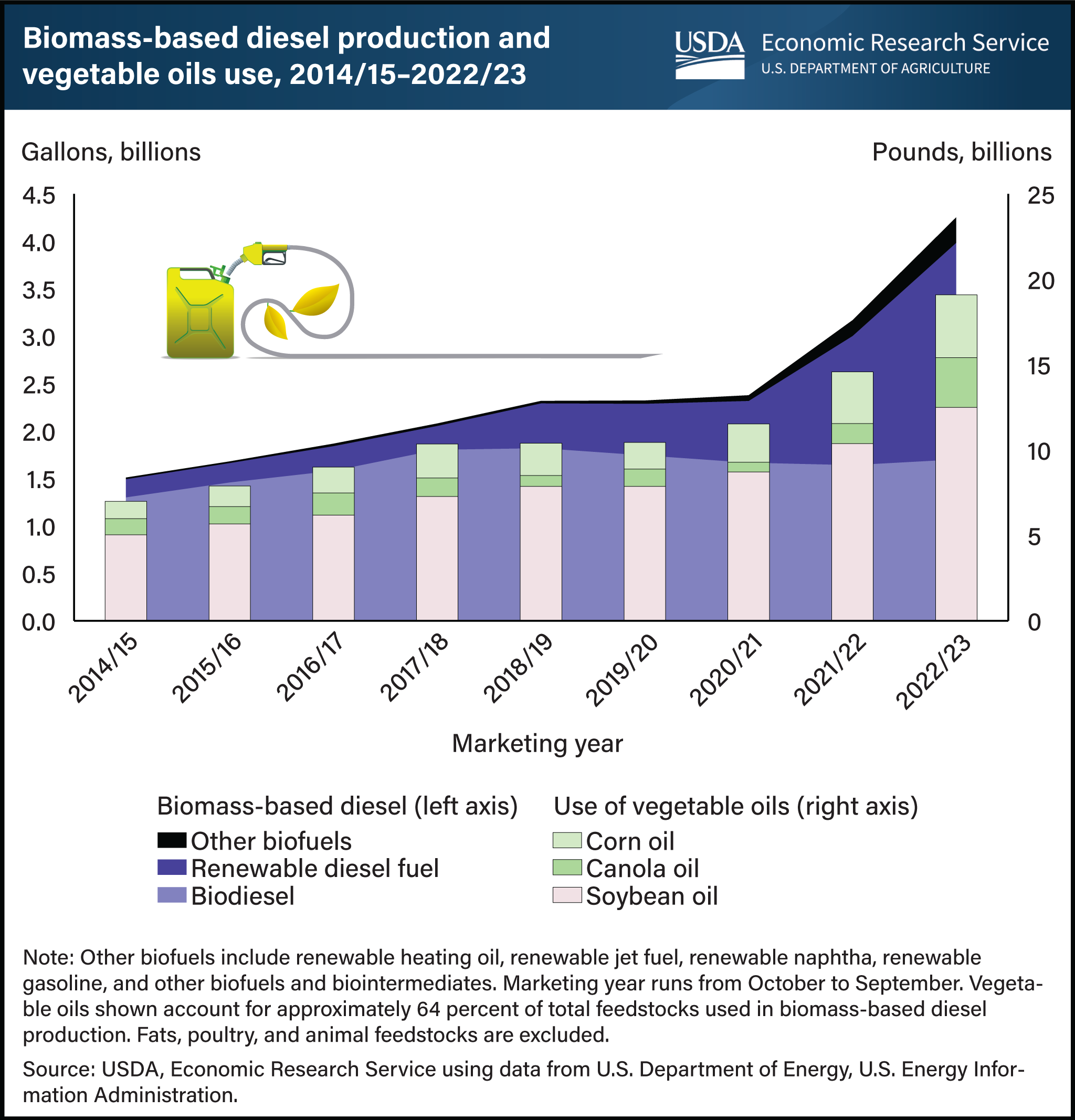
U.S. policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions have encouraged the production of biofuels—fuels derived from crops and animal fats. The policy framework has supported expansion in the production of biomass-based diesel. Biomass-based diesel includes biodiesel and renewable diesel, which now captures the second-largest share of biofuel production, after ethanol. With vegetable oils as the main feedstock in biomass-based diesel production, demand for major vegetable oils (soybean, corn, and canola) for the 2022/23 marketing year (October-September) reached a high of 19.1 billion pounds, up nearly 4.5 billion pounds from 2021/22. Use of soybean oil accounts for more than 40 percent of total feedstocks used for biomass-based diesel production. It increased from 5 billion pounds in 2014/15 to 12.5 billion pounds in 2022/23. Corn and canola oils also are increasingly used in biofuel production, though in lesser amounts. To date, U.S. production of soybean, corn, and canola oils has not been sufficient to cover the rise in domestic use. Rising domestic demand is supported by increasing imports, which now supply more than 29 percent of domestic vegetable oil consumption. This chart is drawn from USDA, Economic Research Service’s Oil Crops Outlook, December 2023.

