Farm sector real estate debt hits record high, sharply diverging from non-real estate debt
- by Monika Ghimire and Carrie Litkowski
- 5/1/2023
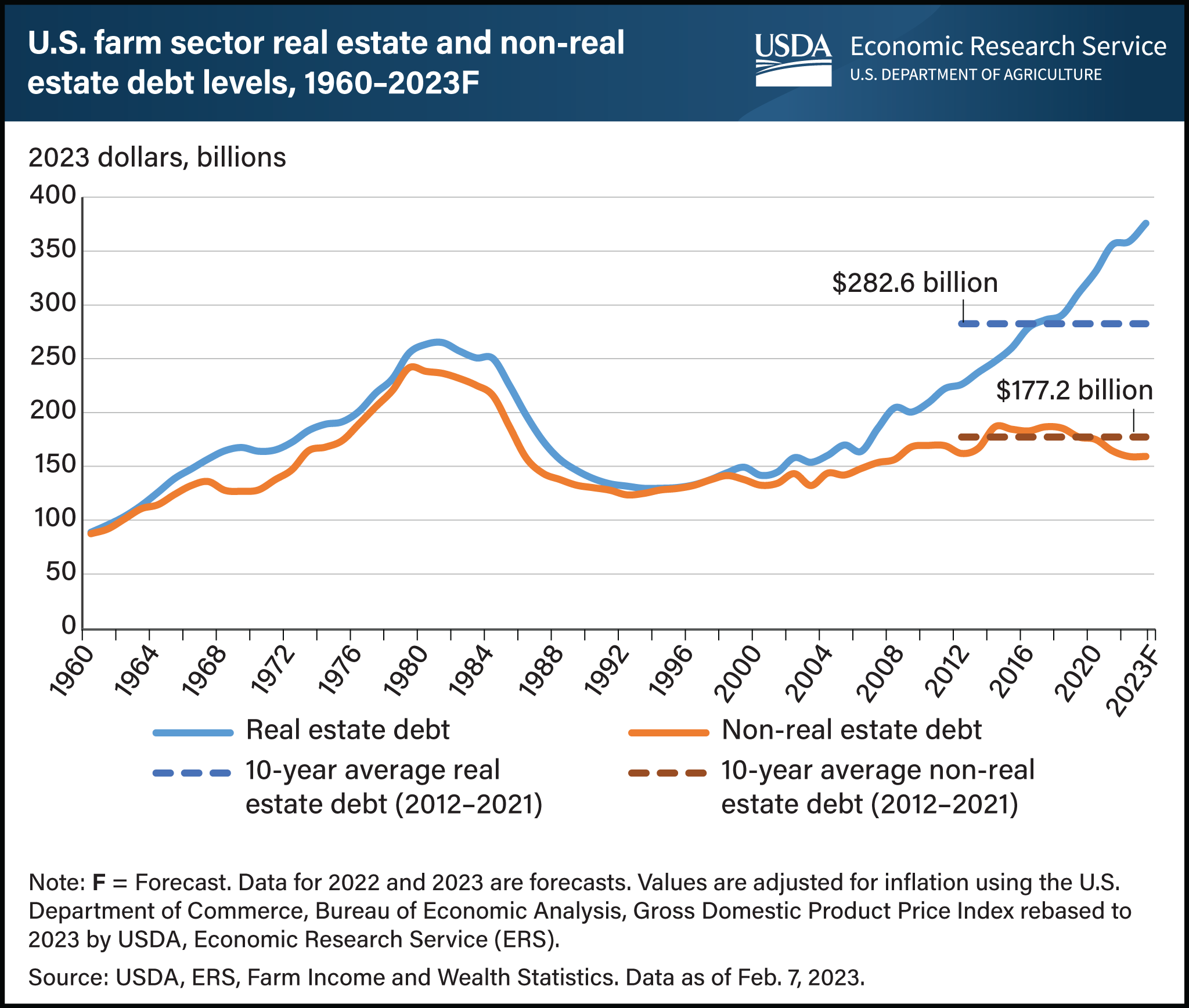
Farm sector debt tied to real estate is expected to be at a record high of $375.9 billion in 2023, according to data from the USDA, Economic Research Service (ERS). Farm sector real estate debt has been increasing continuously since 2009 and is expected to reach an amount that is 87.5 percent higher in 2023 compared with 2009 in inflation-adjusted dollars. Real estate debt now far outpaces debt that is not secured by a mortgage (non-real estate debt). Historically, real estate debt and non-real estate debt have trended similarly, but they have diverged in recent years. Non-real estate debt showed an 11.9-percent year-to-year increase in 2014 in inflation-adjusted dollars but has shown decline after 2017. Meanwhile, there has been a continuous increase in real estate debt since 2009. Growth in farm real estate asset values and relatively low interest rates contributed to the increase in farm real estate debt. In 2023, real estate debt is expected to be 33.0 percent higher than the 10-year average (2012–2021), while non-real estate debt is expected to be 10.2 percent lower than the 10-year average. According to the USDA, National Agricultural Statistics Service’s Land Value 2022 Summary, the average value of farm real estate reached a record $3,800 per acre in 2022, a 12.4-percent increase from 2021. Find information and analysis on ERS’s Farm Sector Income & Finances topic page, which is updated four times a year.

