Self-employed workers were covered more widely across health insurance sources, but many remained uninsured
- by Elizabeth A. Dobis and Jessica E. Todd
- 8/1/2022
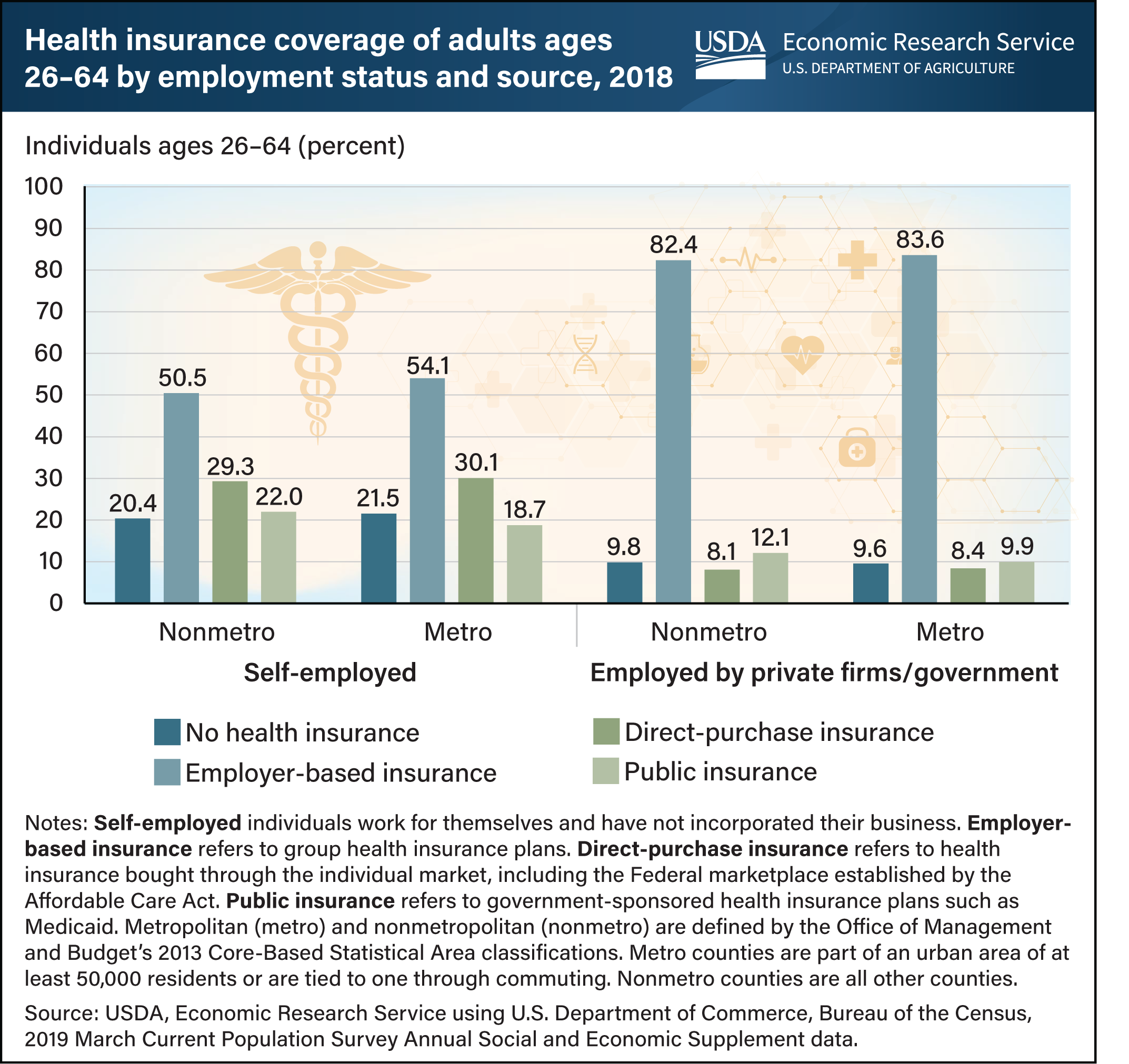
Self-employed workers were more than twice as likely to lack health insurance compared with those employed by private firms or government in 2018, regardless of whether they lived in metropolitan or nonmetropolitan counties. Self-employed working-age adults (ages 26–64) with health insurance were covered more widely across sources. Like those employed by private firms and government, they were insured through employer-based group health insurance plans more than any other source. (Many of these individuals could be receiving coverage through another household member’s employer-based plan.) Even so, a much smaller share of self-employed workers was covered by employer-based plans than those employed by private firms or government (50.5 percent versus 82.4 percent, respectively, in nonmetro counties). Instead, self-employed working-age adults were insured through direct-purchase health insurance plans at more than three times the rate of those employed by private firms or government. Similarly, public health insurance (e.g., Medicaid, Medicare) rates for self-employed working-age adults were nearly twice that of those employed by private firms or government. A version of this chart appears in the ERS publication Health Care Access Among Self-Employed Workers in Nonmetropolitan Counties published May 2022.

