Corn, soybean farmers covered part of their production with futures, options, and marketing contracts in 2016
- by James M. MacDonald
- 3/22/2021
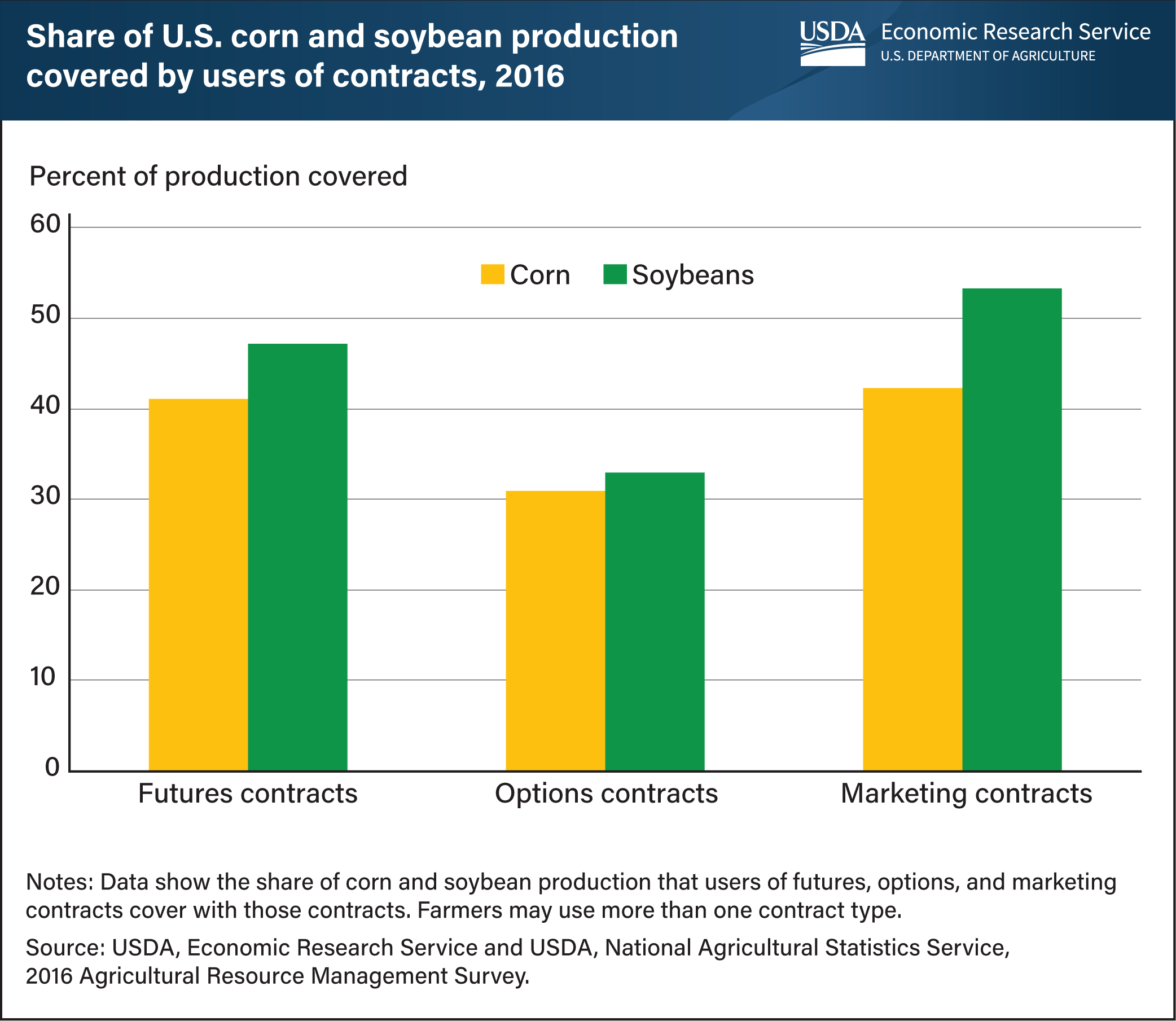
In 2016, corn and soybean producers accounted for about 93 percent of future and options contracts used by U.S. farmers and 60 percent of all production covered by marketing contracts. With a futures contract, a farmer can assure a certain price for a crop that has not yet been harvested. An options contract allows a farmer to protect against decreases in the futures price, while retaining the opportunity to take advantage of increases in the futures price. While futures and options contracts are usually settled without delivery, marketing contracts arrange for delivery of a commodity by a farmer during a specified future time window for an agreed price. Farmers who use these risk management options frequently use more than one contract type. On average, farms that used futures contracts covered 41 percent of their corn production and 47 percent of their soybean production in 2016. Shares were relatively similar for marketing contracts, which covered about 42 percent of corn and 53 percent of soybean production. By comparison, corn and soybean farmers covered a little more than 30 percent of their production with options contracts for both commodities. This chart appears in the Economic Research Service report, Farm Use of Futures, Options, and Marketing Contracts, published October 2020.

